How to verify Smart Contracts Using Block Explorers
Introduction
Usually, the deployer of a smart contract is the only party with access to the code that was actually deployed, and the public cannot read the source code of a contract until the deployer has verified it. However, this is where contract verification comes in as an important step in the smart-contract development cycle, as it helps improve the transparency (for users), convenience (for developers), and security of deployed contracts.
Having said that, once a smart contract is validated, block explorers like Klaytnscope and Klaytnfinder also make it possible for the public to interact with the contract's public methods using the block explorer's user interface. This is in addition to the public having direct access to the verified contract source code.
In this guide, we'll take a look at how to use block explorers to verify deployed smart contracts on the Klaytn Network.
Prerequisites
- Remix IDE and Kaikas Wallet
- Enough test KLAY from faucet
Getting Started
In this guide, we will be going over verifying both single contracts and multi-part contracts on the block explorers that exist in the Klaytn ecosystem, viz.:
Without further ado, let's get started!
Deploying a single Contract
To verify a smart contract, you need to deploy the contract first on the target network. Hence, for the sake of this guide, we will be deploying the contract to Klaytn Baobab Testnet. Also, in this tutorial, we will be deploying a simple counter contract named Counter.sol on Remix IDE. The code is shown below:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;contract Counter { uint256 public count; constructor(uint256 _initialCount) { count = _initialCount; } function incrementCounter() public { count++; } function decrementCounter() public { count--; } function resetCounter() public { count = 0; }}
Parameters for single contract verification
Verifying a contract on the block explorers requires some parameters, and these must be considered while deploying the smart contract. The following are some details related to the contract's compiler and deployment in order to verify a contract successfully:
Remix IDE :
-
On Remix IDE, navigate to the Solidity compiler tab.
- Observe the compiler version used to compile and deploy the contract.
- Observe the Open Source License Type used in the contract. This means the SPDX license identifier used at the beginning of the Solidity source file. In the
Counter.solfile we used// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT - Observe the EVM version used for deploying contracts.
- (Optional) If optimization is enabled during compilation, take note of the value of the optimization runs parameter

-
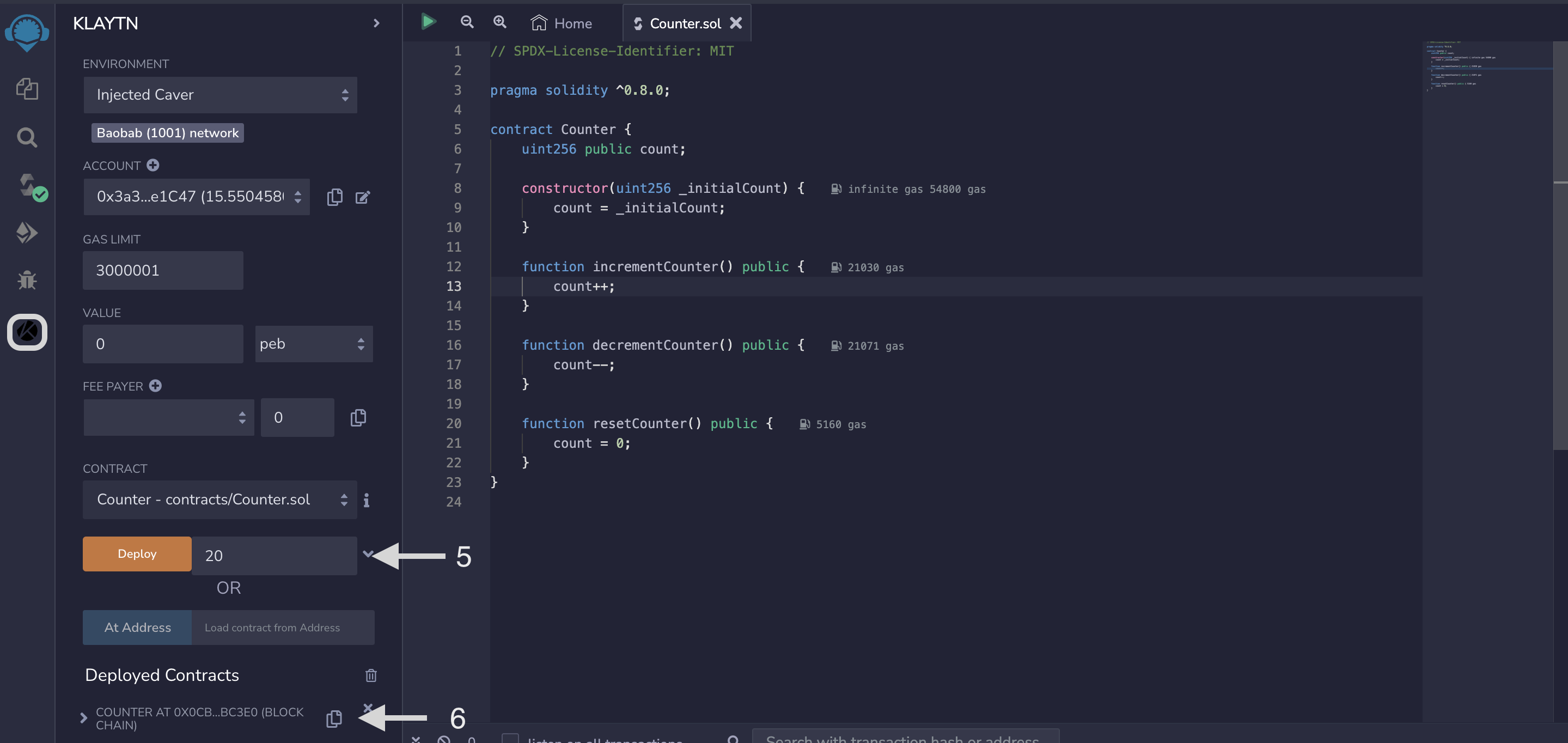
On Remix IDE, navigate to Klaytn tab.
- (Optional) If the contract constructor method accepts arguments, take note of the ABI-encoded form of the constructor arguments
- Take note of the contract address of the smart contract on the Deployed Contracts tab after successful deployment.
Deploying a multi-part contract
It is important to note that deploying a multi-part contract involves the same steps as deploying a single contract. For the sake of this guide, we will be deploying a simple KIP7 airdrop contract named airdropToken.sol. The code is shown below:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.4;import "@klaytn/contracts/KIP/token/KIP7/KIP7.sol";import "@klaytn/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";// the creator of the project mints certian amount of fungible tokens directly to a certain selection of wallets.contract TokenAirdrop is KIP7, Ownable { constructor() KIP7("Token Aidrop Demo", "TAD") { } // Airdrop Token function airdropTokens(address[] calldata wAddresses, uint[] calldata tAmount) public onlyOwner { require(wAddresses.length == tAmount.length, "Must be same lenght"); for (uint256 i = 0; i < wAddresses.length; i++) { _mintSingleTokens(wAddresses[i], tAmount[i]); } } function _mintSingleTokens(address wAddress, uint amount) private { _mint(wAddress, amount); } function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view virtual override returns (bool) { return super.supportsInterface(interfaceId); }}
Parameters for multi-part contract verification
The parameters for verifying a multi-part contract are the same as those for a single contract. However, because they are made up of multiple dependent contracts, we need to pre-process all dependencies of the contract into a single solidity file. This preprocessing is usually referred to as smart contract flattening.
For this reason, we will have to flatten the contract so it can be verified using the new flattened Solidity file on the block explorer.
Remix IDE:
-
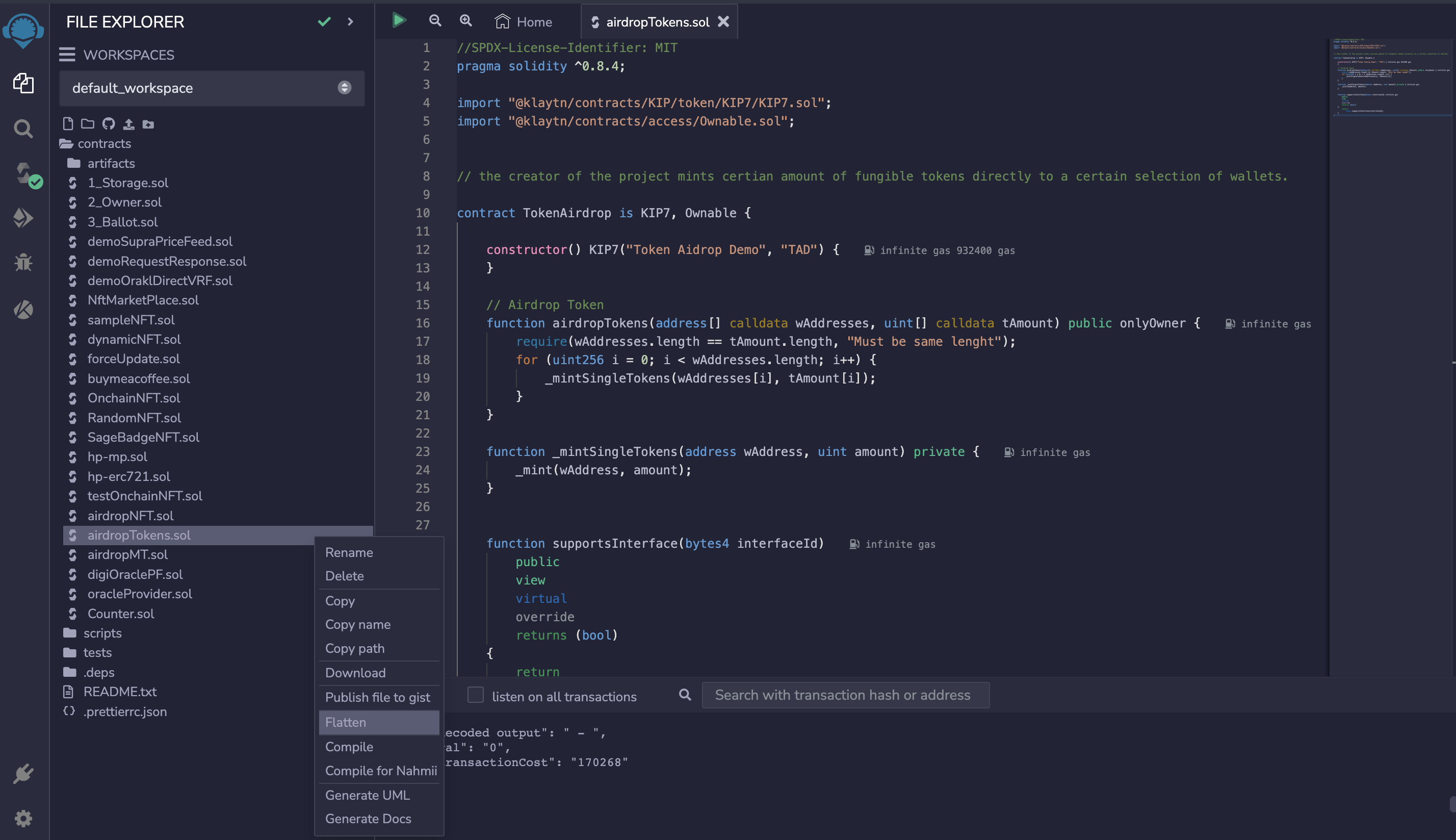
On Remix IDE, navigate to the File explorer tab.
- Select the newly created contract under the contracts folder
- Click or tap with two fingers to see all commands available on the contract.
- Select flatten
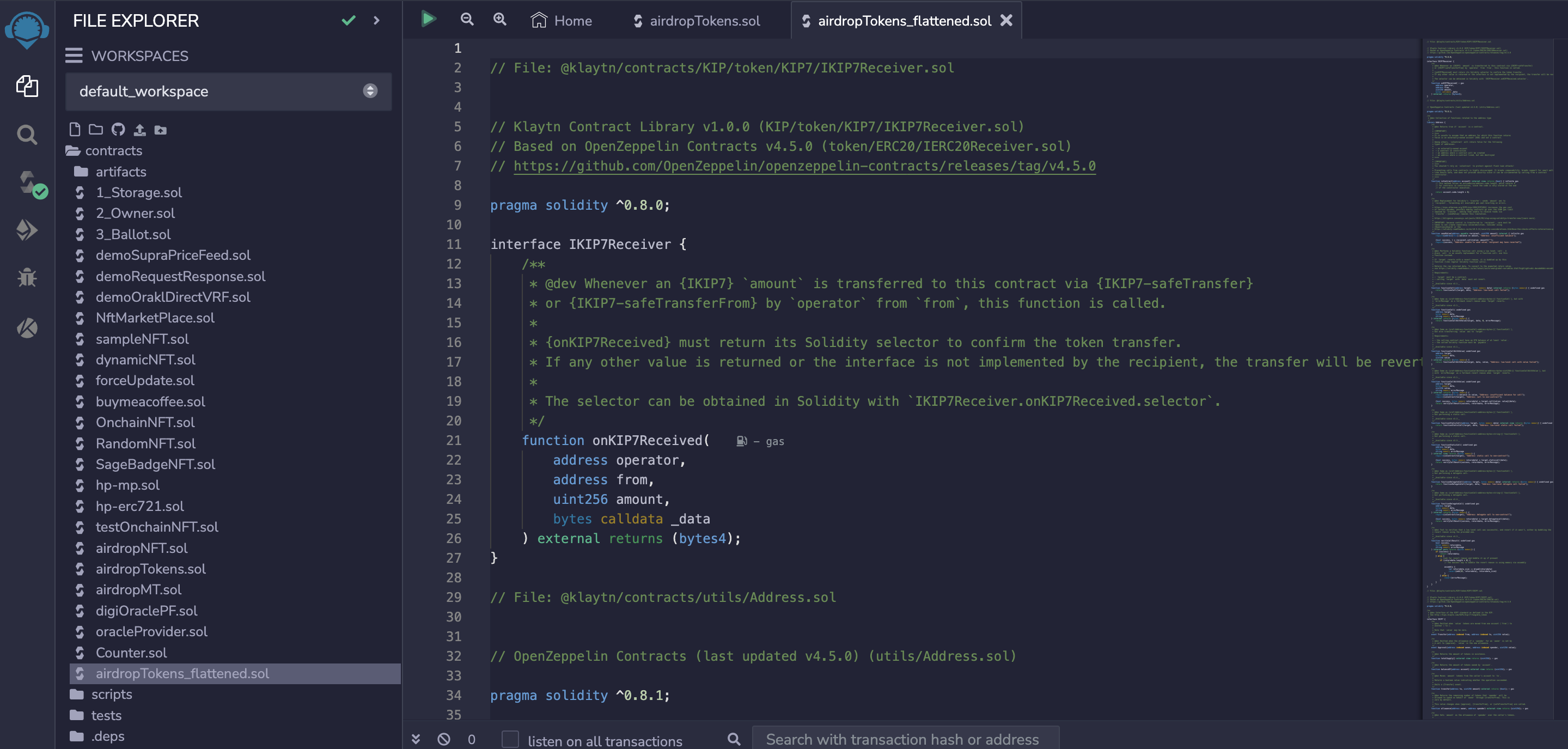
- Once code is flattened, you will see a new contract named
airdropTokens_flattened.sol.
There are different tools for flattening a multi-part smart contract into a single Solidity file, such as Hardhat Flattener. Kindly refer to the respective smart contract flattening tool's documentation for more detailed instructions on its usage.
Verifying the Contract
Having obtained all of our verification parameters, we will go over the steps for verifying a single smart contract (Counter.sol) and a multi-part smart contract (airdropTokens.sol) on the block explorer in this section.
1. Klaytnscope
To verify a single contract and multi-part contracts on Klaytnscope, follow the steps below:
1.1 Verifying a single contract
- Goto the search bar of Klaytnscope and paste the deployed contract address.
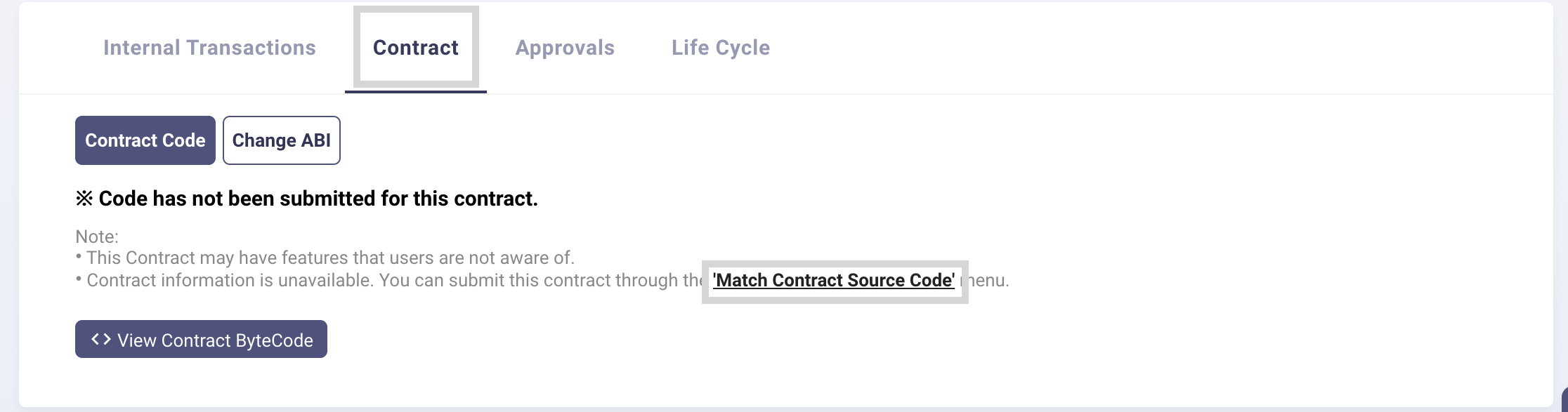
- Navigate to the contract tab on that page.
- Click on the Match Contract Source Code link to submit contract code for verification.
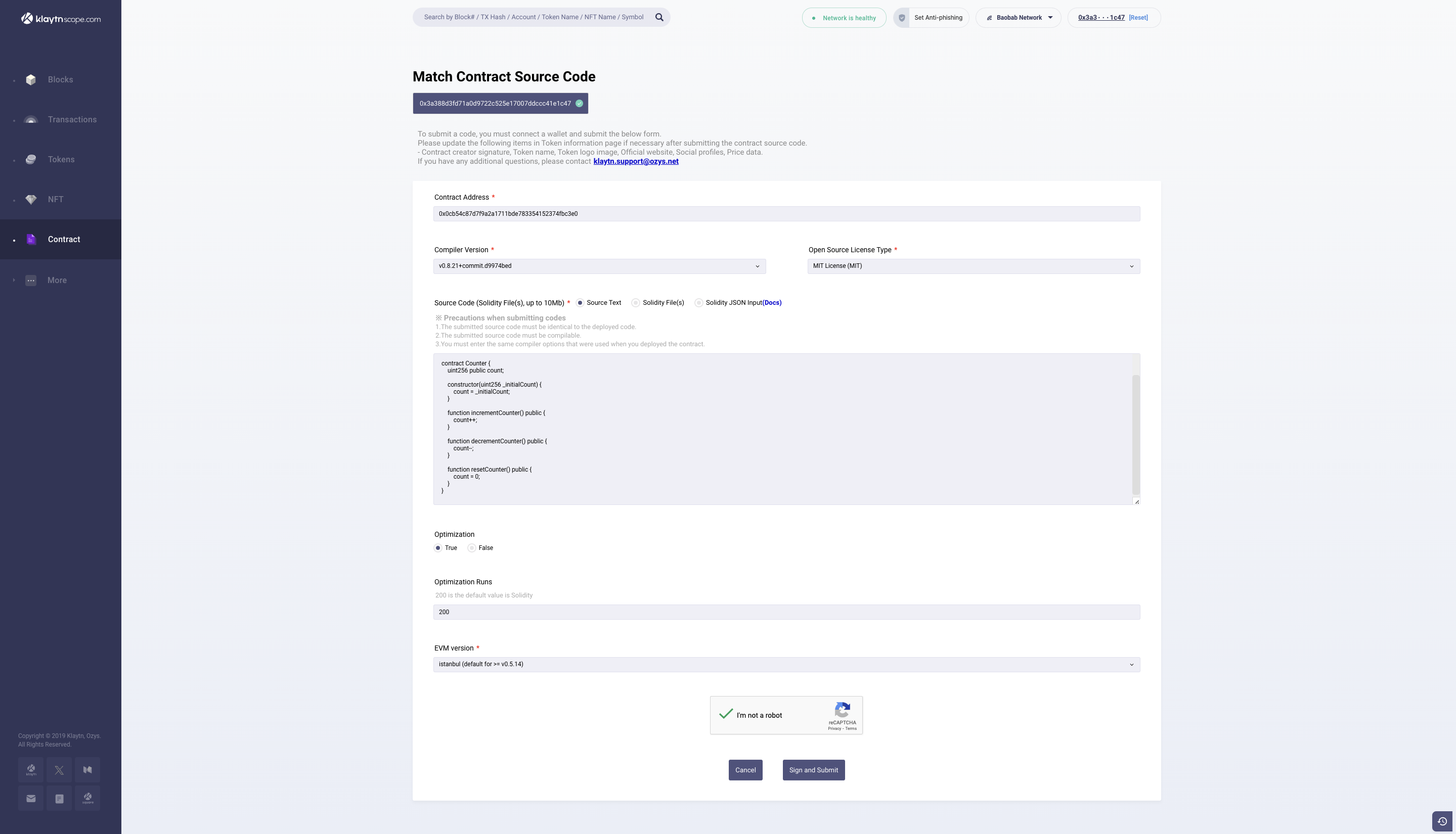
- On the contract verification page, make sure your account is connected to either Kaikas or Metamask. For this guide, we will be using Kaikas.
- Fill in the contract address in the contract address field. Note: This field is usually filled with the contract address automatically.
- Select the compiler version used for the
Counter.solexample. - Select the Open Source License Type used for the
Counter.solexample. ForCounter.solexample, select the option, MIT License (MIT). If there was none used, select No License (None). - In the Source Code field, select Source Text and paste the source code for
Counter.solin the text-field. - Select True for Optimization if it was enabled during compilation, and fill in the number of runs under Optimization Runs to be 200.
- Select the EVM version for the contract. For
Counter.solexample, select the option Istanbul. - Click on the CAPTCHA at the bottom and the Sign and Submit button to confirm and begin verification.
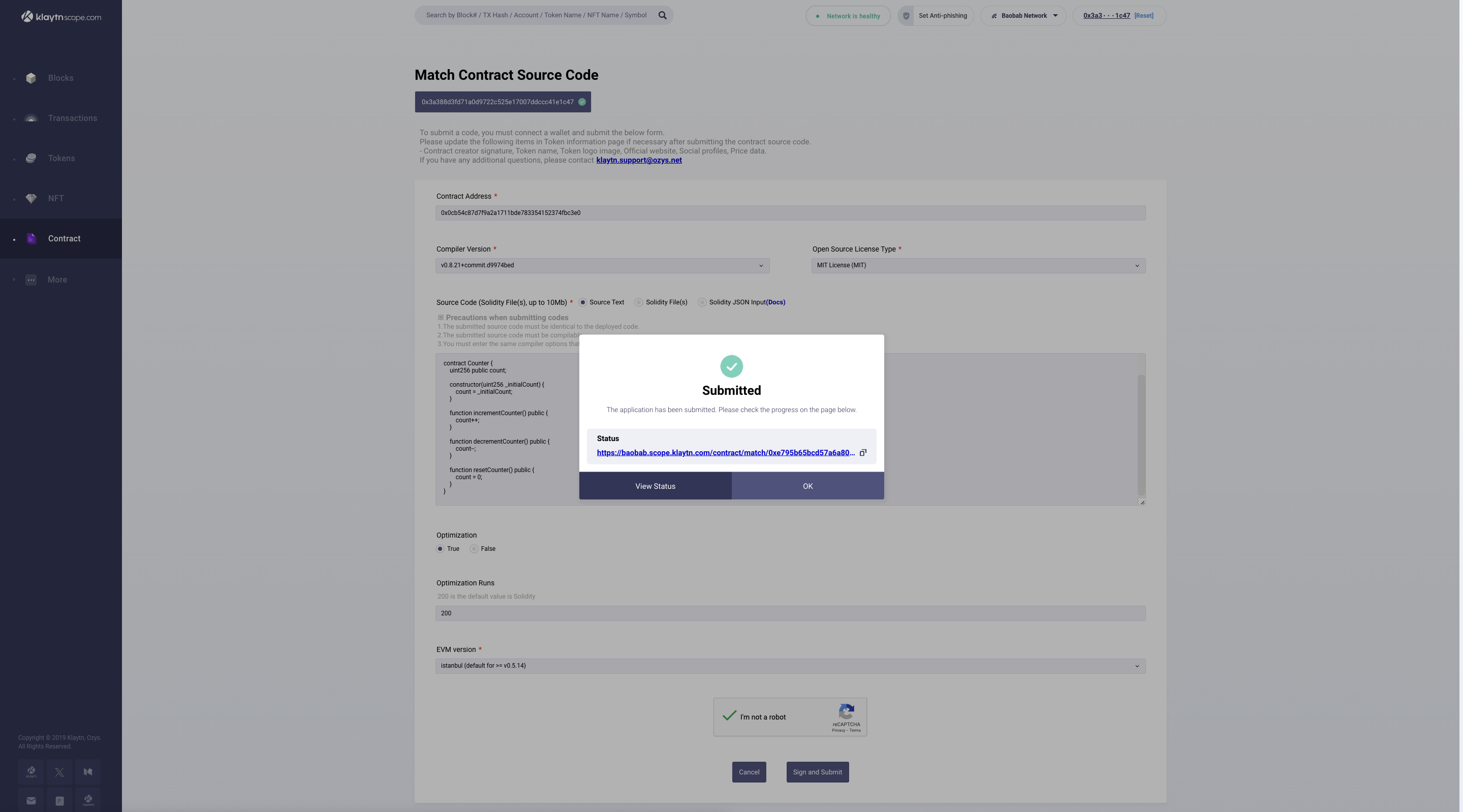
- After signing the verification request, you will get a verification status notification
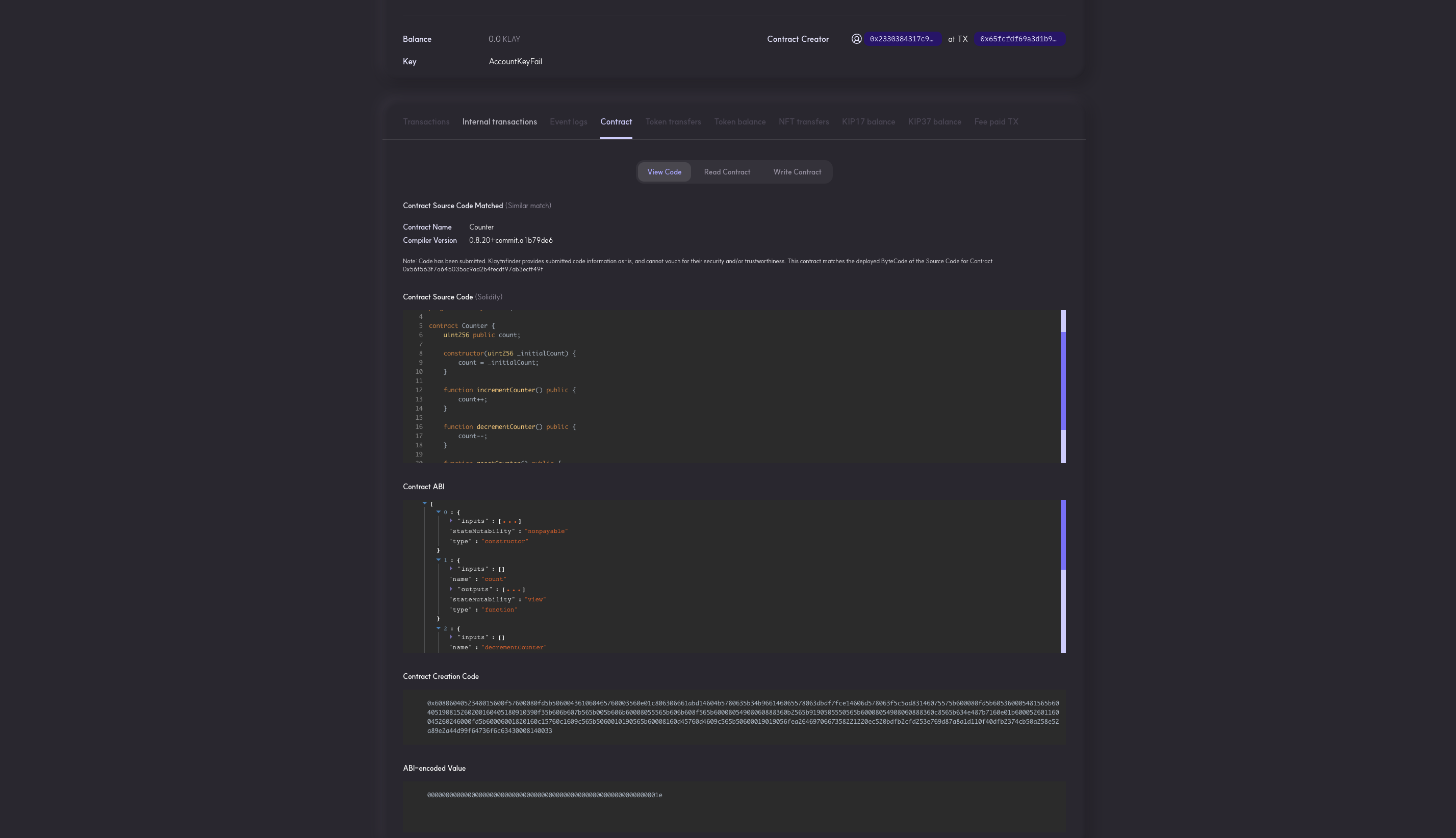
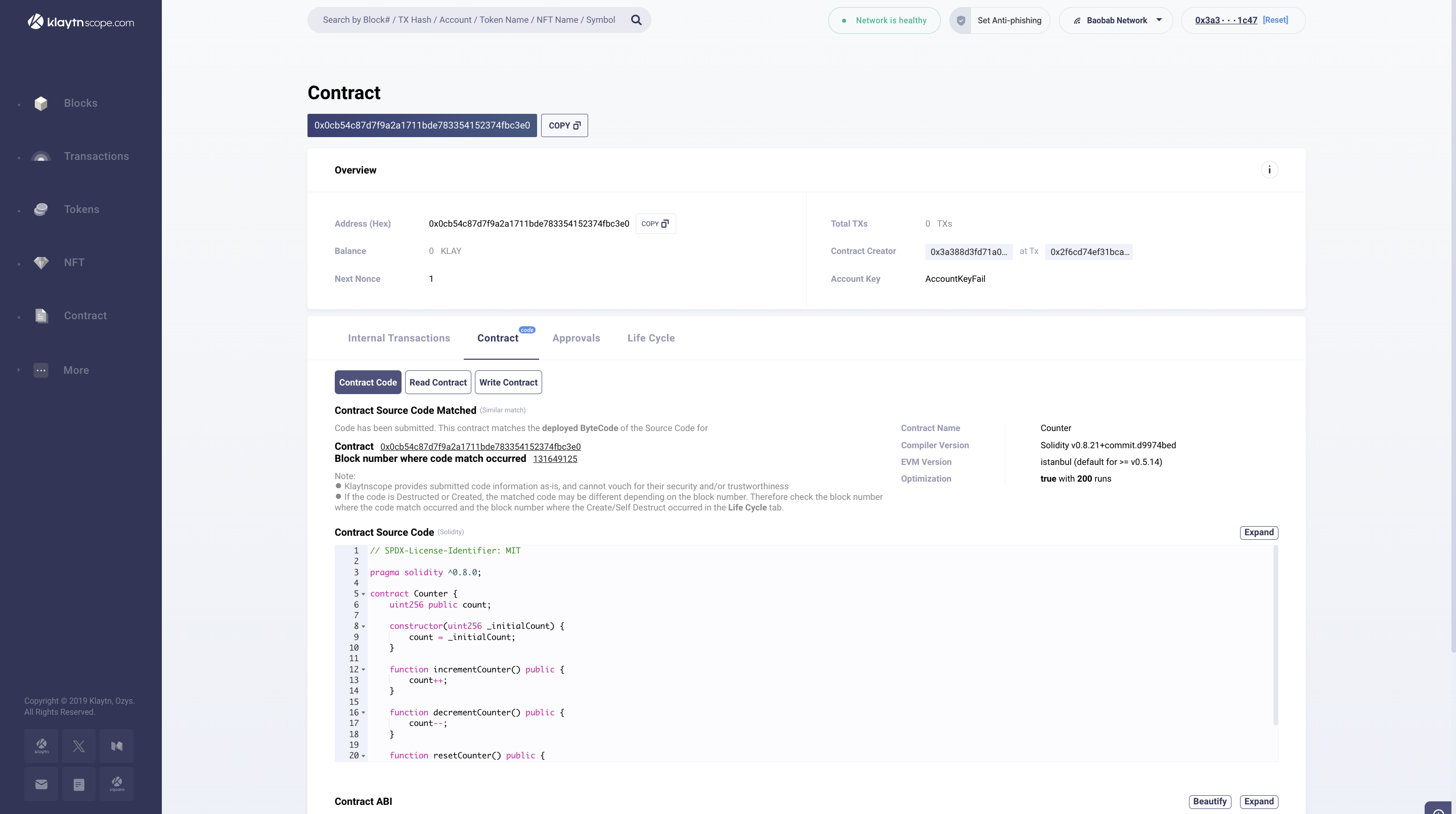
- Once verification is done, the result of the verification will be displayed in the browser, and a success result page with the contract address. Click on the contract address to view the Contract Source Code, Contract ABI, and Bytecode.

1.2 Verifying multi-part contract
Verifying a multi-part contract on Klaytnscope is as straightforward as verifying a single contract, except that it requires some additional steps. In this section, we will be verifying the airdropToken.sol contract with the following additional steps:
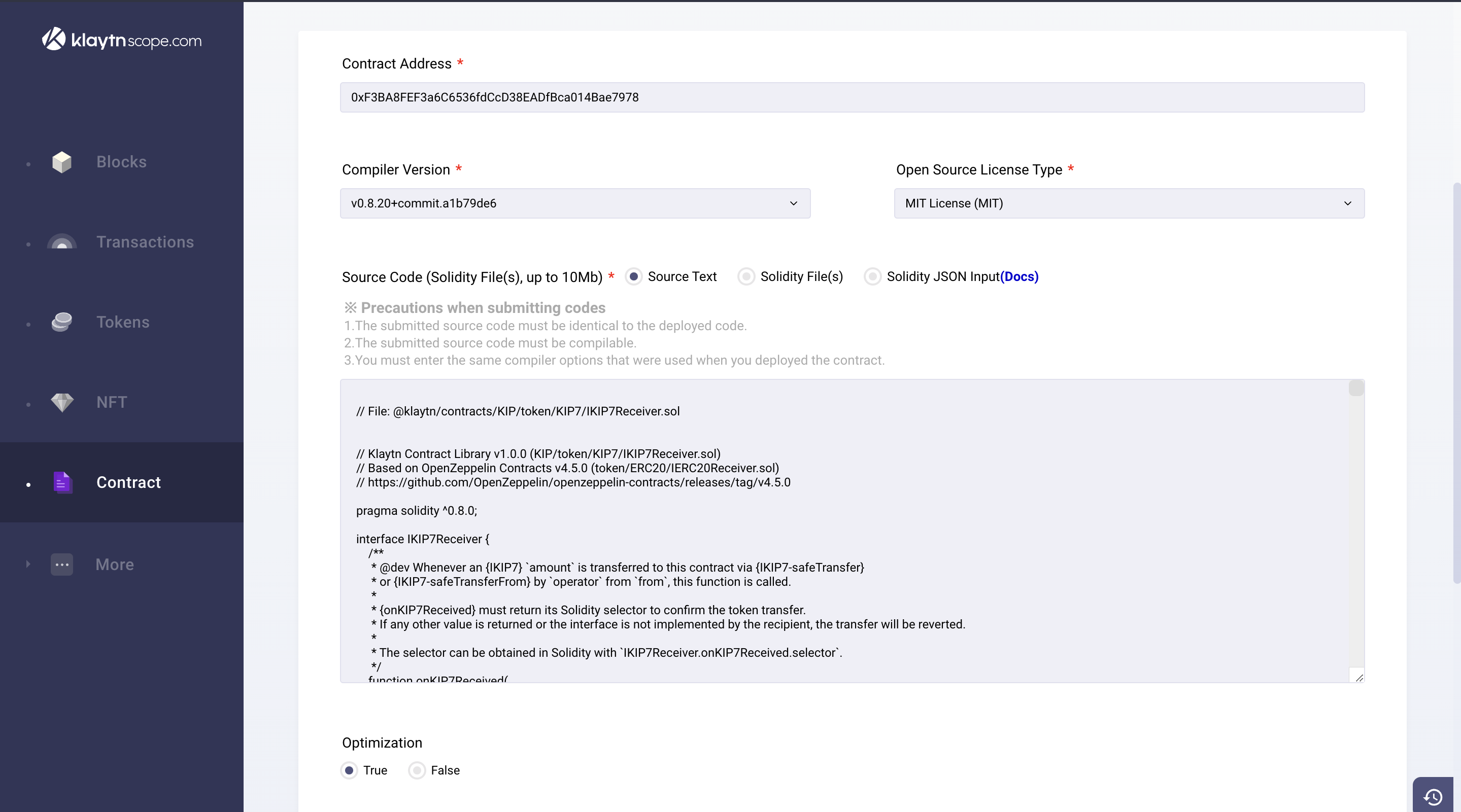
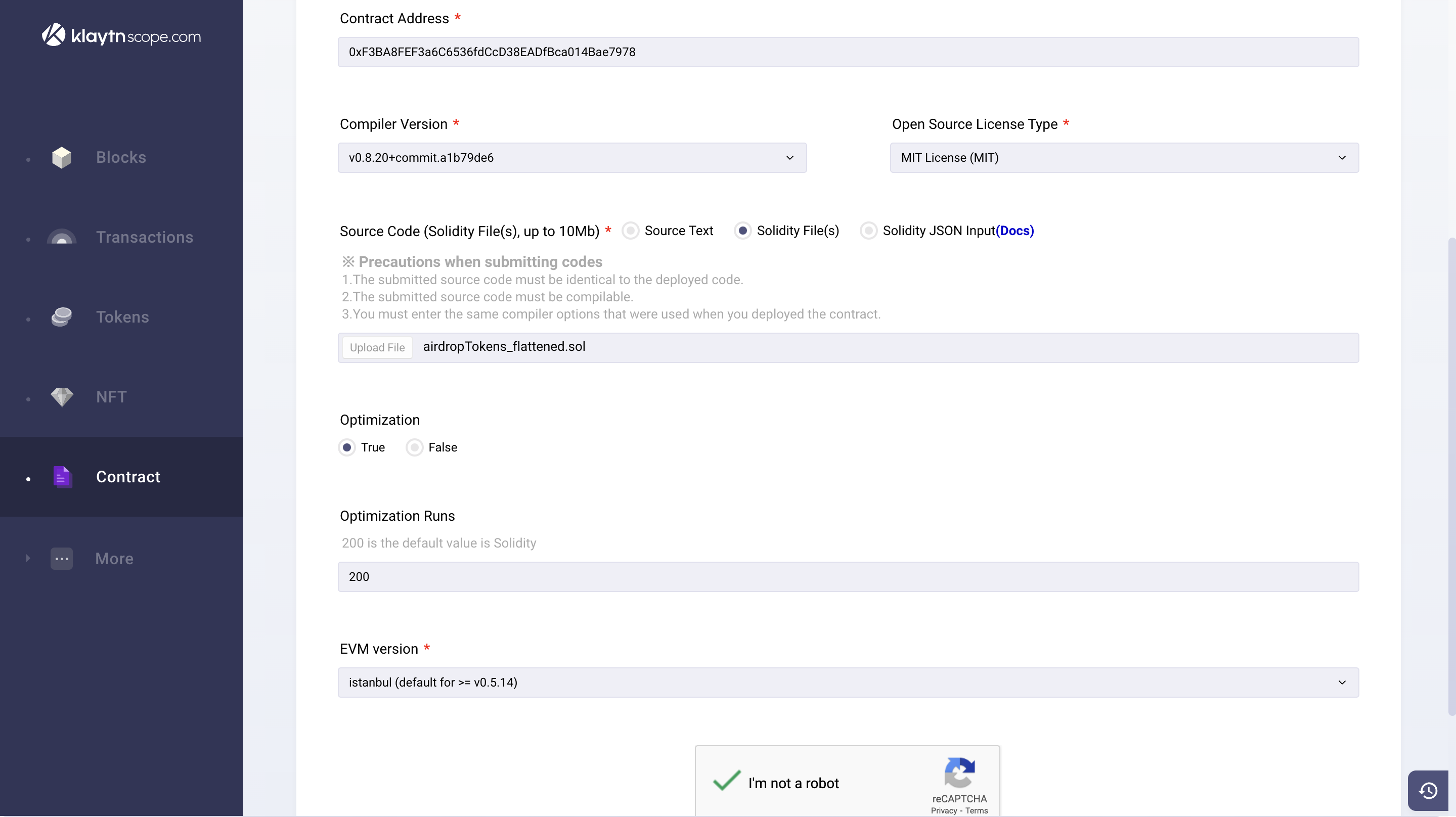
- You can either Select Source Text under Source Code (step 3 of the Counter.sol example) or Solidity File(s) under the Source Code field. In the case of Source Text, copy the code in the
airdropToken_flattened.soland paste in the text field. If Solidity File(s), you can download theairdropToken_flattened.solfile on Remix IDE and upload to the field.
a. Source Text
b. Solidity File(s)
After this, every other step remains the same as verifying a single contract. Having filled the verification parameter, click on the Sign and Submit button to confirm and begin verification.
Once verification is done, the result of the verification will be displayed in the browser, and a success result page with the contract address. Click on the contract address to view the Contract Source Code, Contract ABI, and Bytecode.

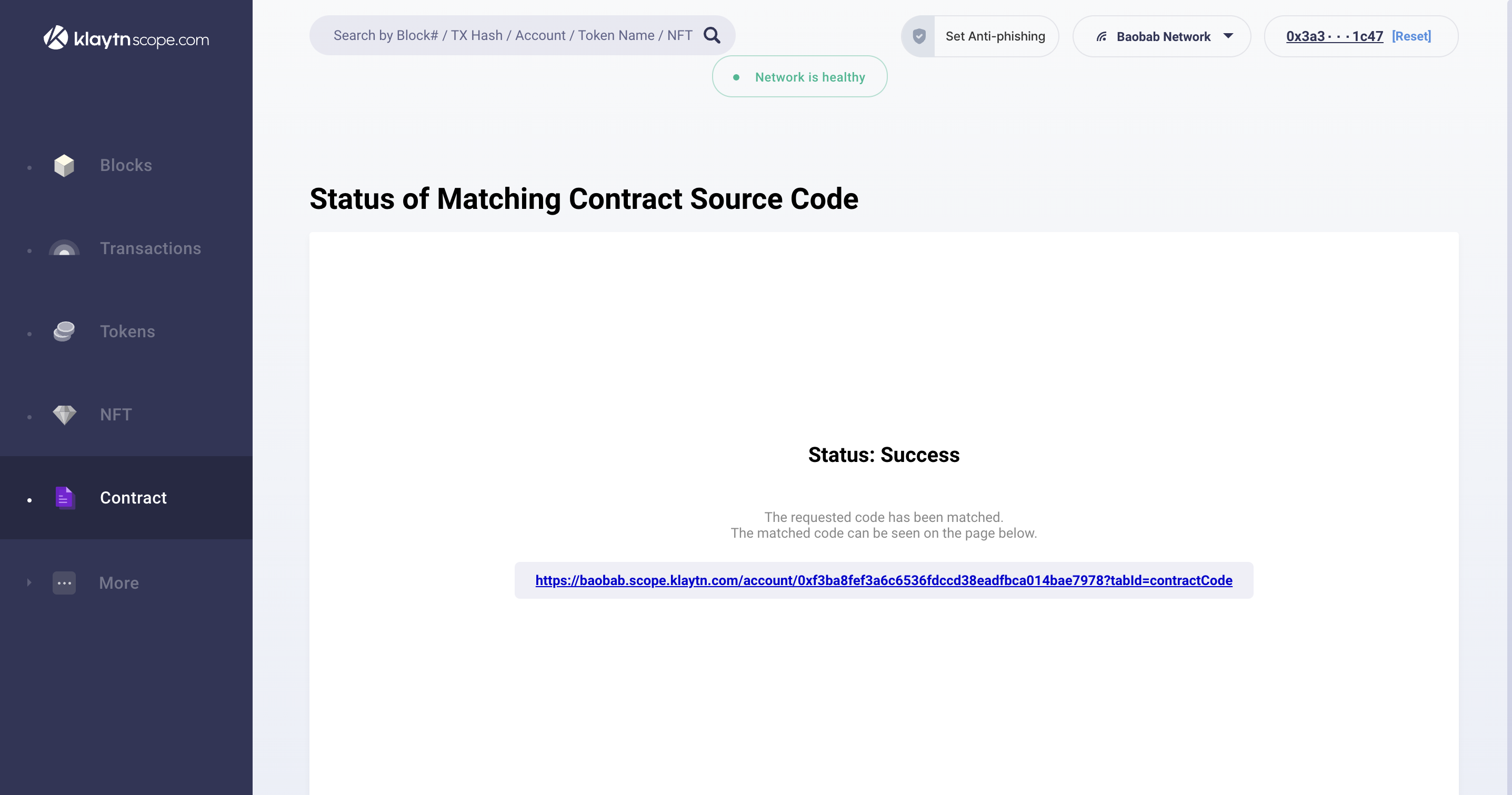
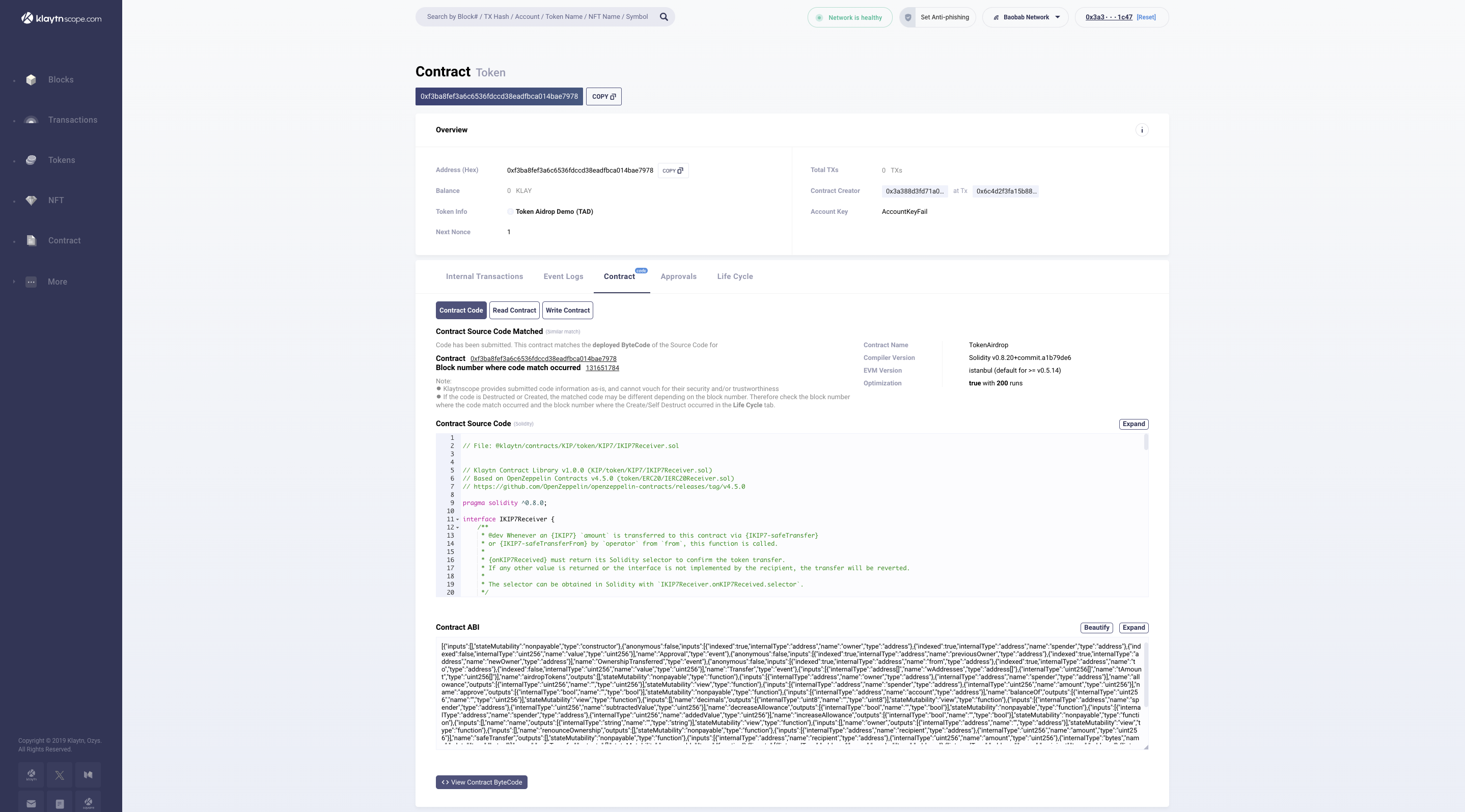
2. Klaytnfinder
To verify a single contract and multi-part contracts on Klaytnfinder, navigate to the contract submission request page. However, make sure your account is connected to either Kaikas or MetaMask and follow the steps below:

2.1 Verifying single contract
- Observe the Is this contract for a token field? This field is needed when trying to verify a token contract with its official website URL, official email address, and token logo image. For the sake of this guide, select No as we are not verifying a commercial token contract.
- Fill in the contract address for the deployed contract (Counter.sol)
- Make sure to download
Counter.solfrom Remix IDE and upload in the Source Code (Solidity File) field - Select the compiler version used for the
Counter.solexample - Select the Open Source License Type used for the
Counter.solexample. ForCounter.solexample, select the option, MIT License (MIT). If there was none used, select No License (None) - Select the EVM version for the contract. For
Counter.solexample, select the option Istanbul. - Select True for Optimization if it was enabled during compilation, and fill in the number of runs under Optimization Runs to be 200.
- (optional) To get the ABI-encoded constructor arguments for this field, navigate to abi.hashex.org to get the encoded data following the image below:

- Click on the Sign and Submit button to confirm and begin verification.
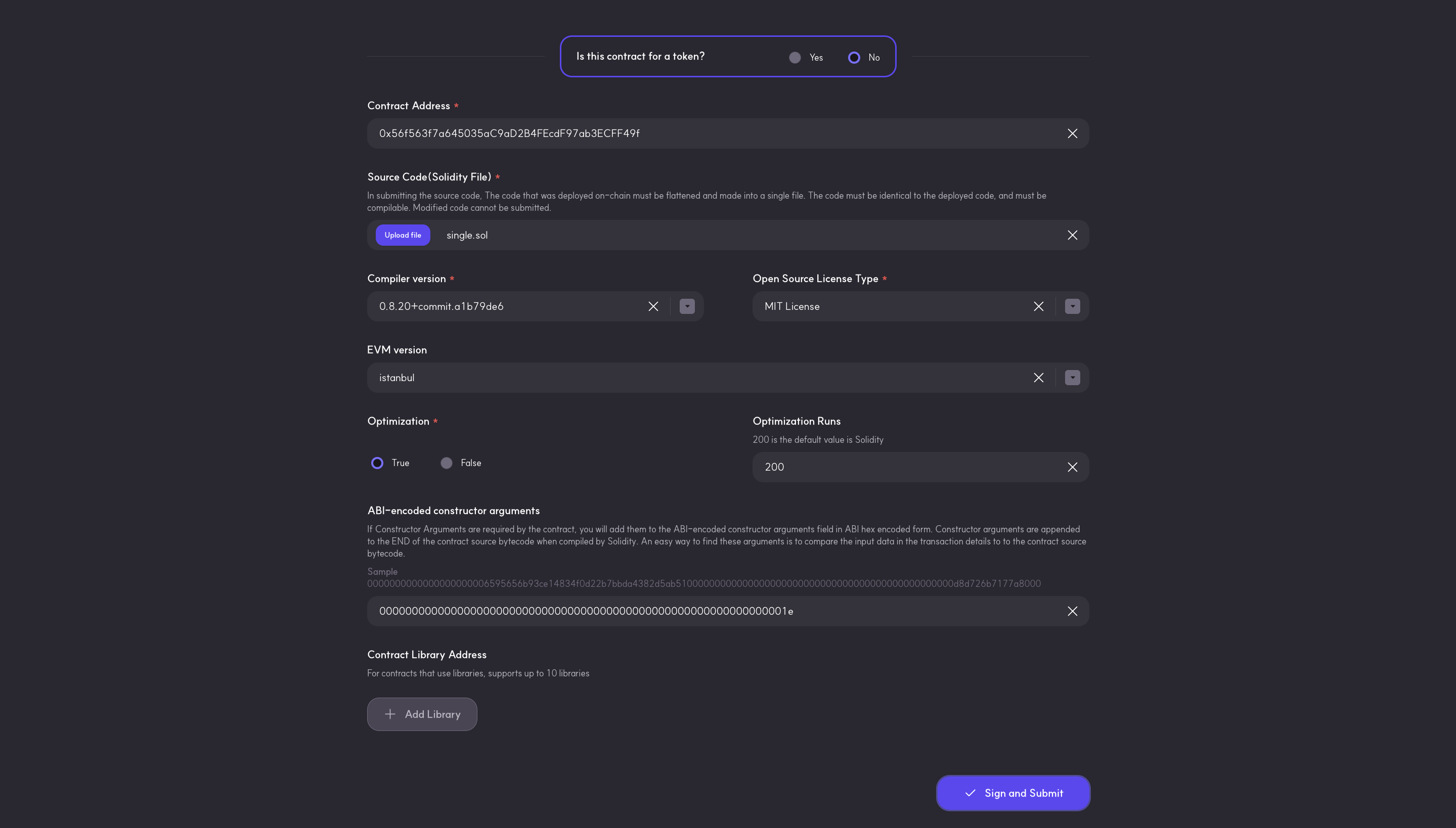
- Once verification is done, you will get a Submission Successful message. Now you can paste the contract address in the explorer search bar to view the Contract Source Code, Contract ABI, Creation Code and ABI-encoded Value.
2.2 Verifying multiple-part contract
Verifying a multi-part contract on Klaytnfinder follows the same step as verifying a single contract. However, it is important to note we will be uploading the airdropToken_flattened.sol file in the Source Code(Solidity File) field.
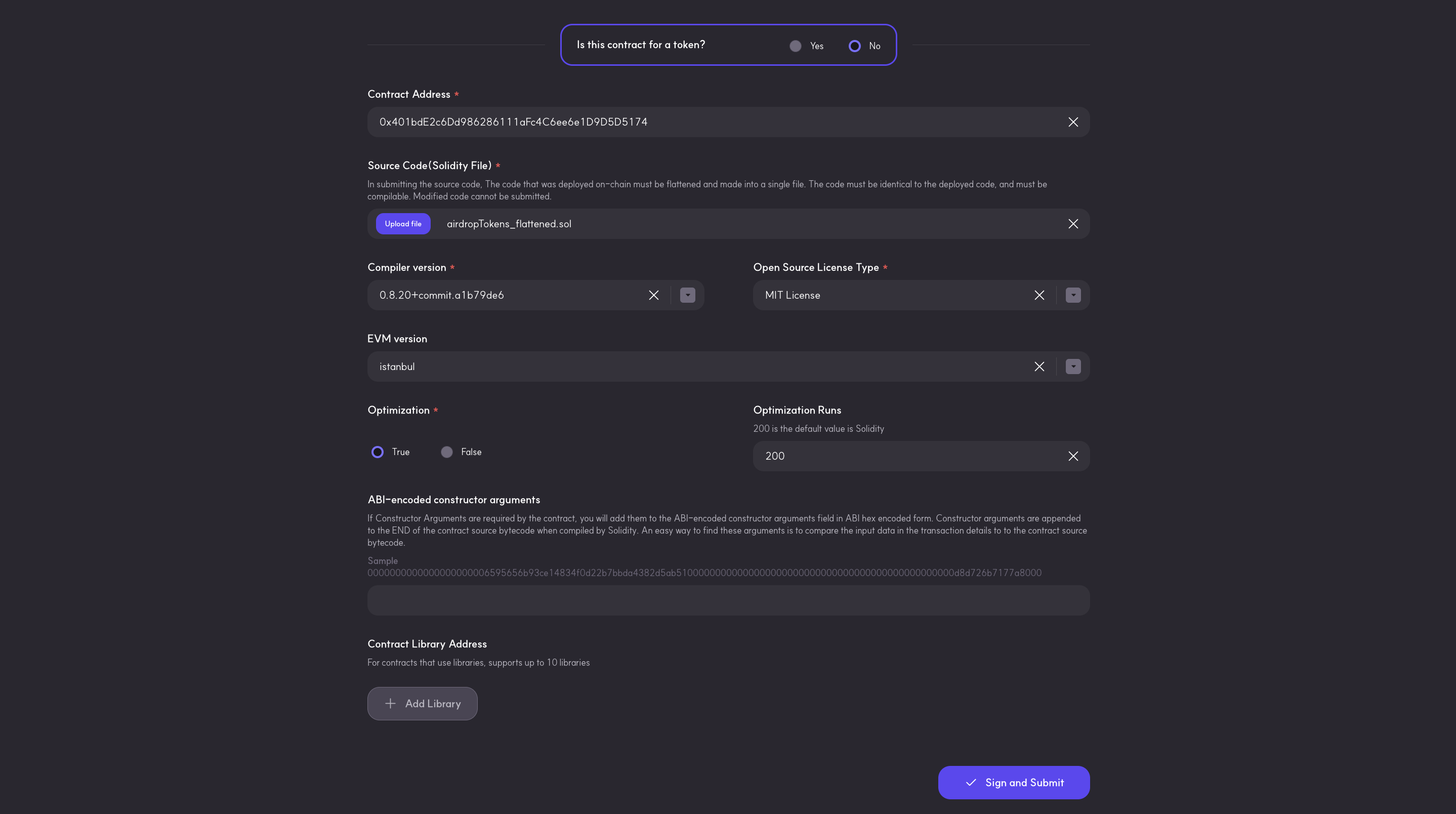
After filling the verification parameters, click on the Sign and Submit button to confirm and begin verification. Once verification is done, you will get a Submission Successful message. Now you can paste the contract address in the explorer search bar to view the Contract Source Code, Contract ABI, and Creation Code.
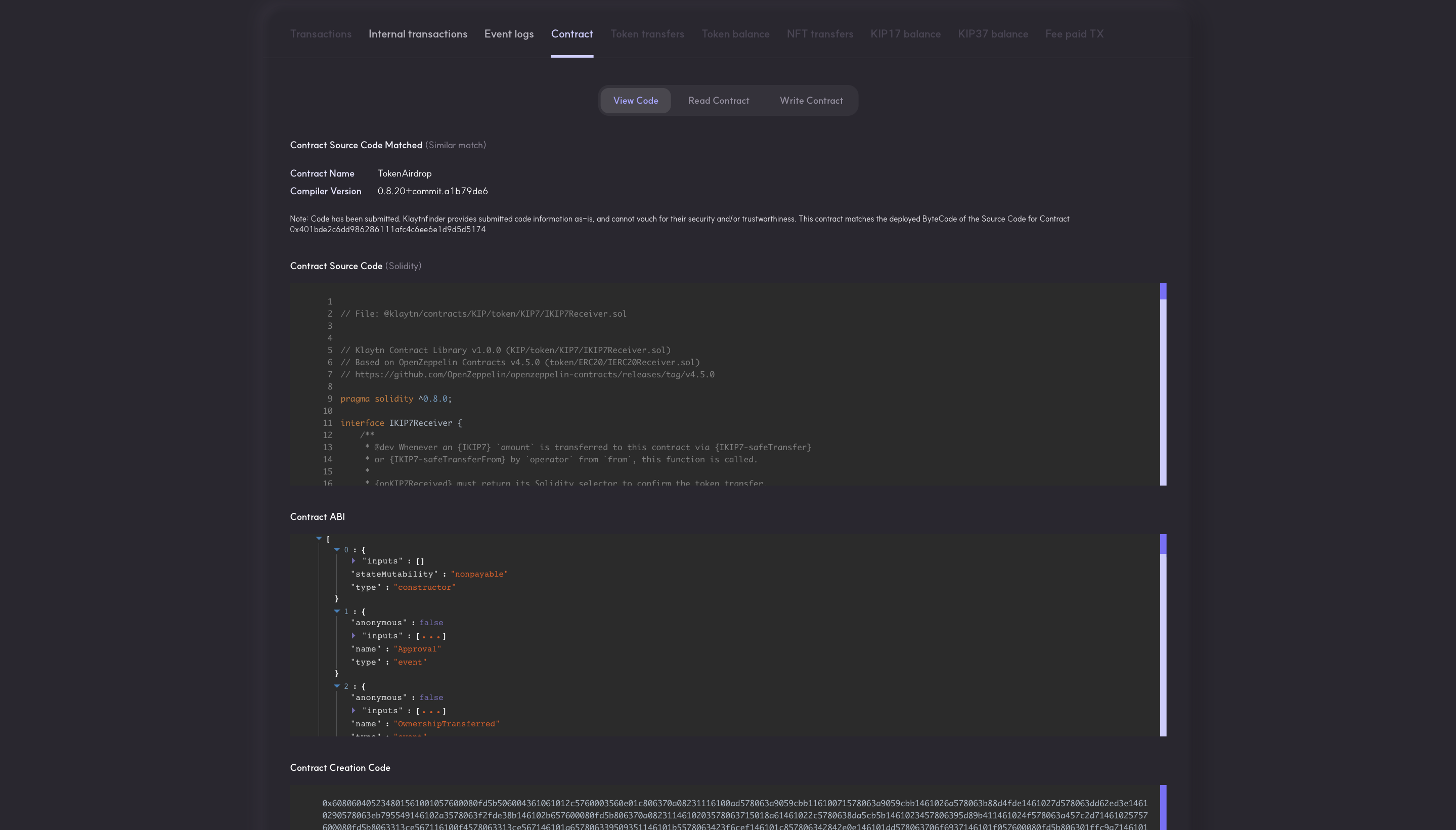
Conclusion
Congratulations on following this guide! In this tutorial, you learnt how to verify contracts (both single and multi-part) using Klaytnscope and Klaytnfinder solely to enhance the transparency (for users), convenience (for developers), and security of deployed contracts. Visit Klaytn Docs for more information and Klaytn Forum if you have any questions.