Migrate Ethereum App to Klaytn
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Klaytn has Ethereum compatibility
- 3. Change node connection from Ethereum to Klaytn
- 4. Interact with Klaytn node:
BlockNumbercomponent - 5. Interact with the contract:
Countcomponent
1. Introduction
This tutorial is intended to give a guide to migrate an Ethereum App to Klaytn. No previous Klaytn experience is needed. A simple blockchain app will be used as a sample to show how to migrate an Ethereum App to Klaytn.
We will focus only on the code modifications required to migrate an Ethereum App to Klaytn. If you need details on creating a Klaytn dApp, Please refer to CountDApp Tutorial.
Source Code
Complete source code can be found on GitHub at https://github.com/klaytn/countbapp
Intended Audience
- We assume that you have basic knowledge on React. Sample code is made with React.
- Basic knowledge and experience in Blockchain app is required, but no previous Klaytn experience is needed.
Testing Environment
CountDApp is tested in the following environment.
- MacOS Mojave 10.14.5
- Node 10.16.0 (LTS)
- npm 6.9.0
- Python 2.7.10
2. Klaytn has Ethereum compatibility
Klaytn runtime environment is compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine and executes smart contracts written in Solidity. Klaytn's RPC APIs and other client libraries maintain almost identical API specifications with Ethereum's whenever available. Therefore, it is fairly straightforward to migrate Ethereum Apps to Klaytn. This helps developers easily move to a new blockchain platform.
3. Change node connection from Ethereum to Klaytn
First, you need to change the library that makes a connection to the node. Then you will specify the node URL in 'rpcURL'. (FYI. The Ropsten testnet in ethereum will be shut down in Q4 2022. )
- Ethereum
web3library connects to and communicates with Ethereum node.Ropsten testnetURL is assigned to 'rpcURL' .
- Klaytn
caver-jslibrary is used to connect to and communicate with Klaytn node.Baobab testnetURL is assigned to 'rpcURL'.
src/klaytn/caver.js
// import Web3 from 'web3'import Caver from 'caver-js'// const ROPSTEN_TESTNET_RPC_URL = 'https://ropsten.infura.io/'const BAOBAB_TESTNET_RPC_URL = 'https://public-en-baobab.klaytn.net/'// const rpcURL = ROPSTEN_TESTNET_RPC_URLconst rpcURL = BAOBAB_TESTNET_RPC_URL// const web3 = new Web3(rpcURL)const caver = new Caver(rpcURL)// export default web3export default caver
4. Interact with Klaytn node: BlockNumber component

BlockNumber component gets the current block number every 1 second (1000ms).
By simply replacing the web3 library with caver-js, you can sync Klaytn's BlockNumber in real-time instead of Ethereum's BlockNumber.
Ethereum:
web3.eth.getBlockNumber()
Klaytn:caver.klay.getBlockNumber()
// import web3 from 'ethereum/web3'import caver from 'klaytn/caver'class BlockNumber extends Component { state = { currentBlockNumber: '...loading' } getBlockNumber = async () => { // const blockNumber = await web3.eth.getBlockNumber() const blockNumber = await caver.klay.getBlockNumber() this.setState({ currentBlockNumber: blockNumber }) } // ...}export default BlockNumber
For more detail about BlockNumber component, see CountDApp tutorial - Blocknumber Component.
5. Interact with the contract: Count component
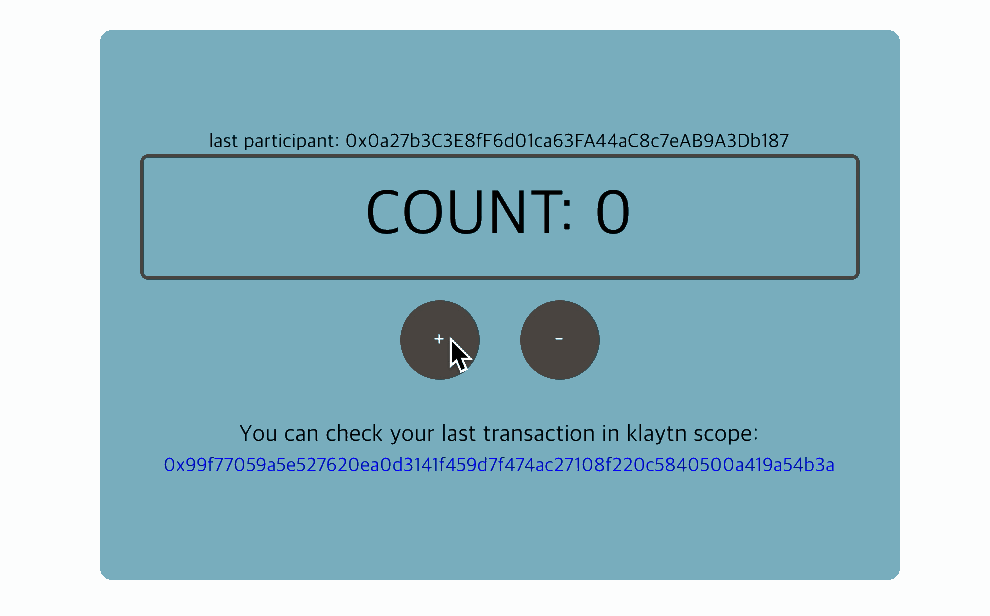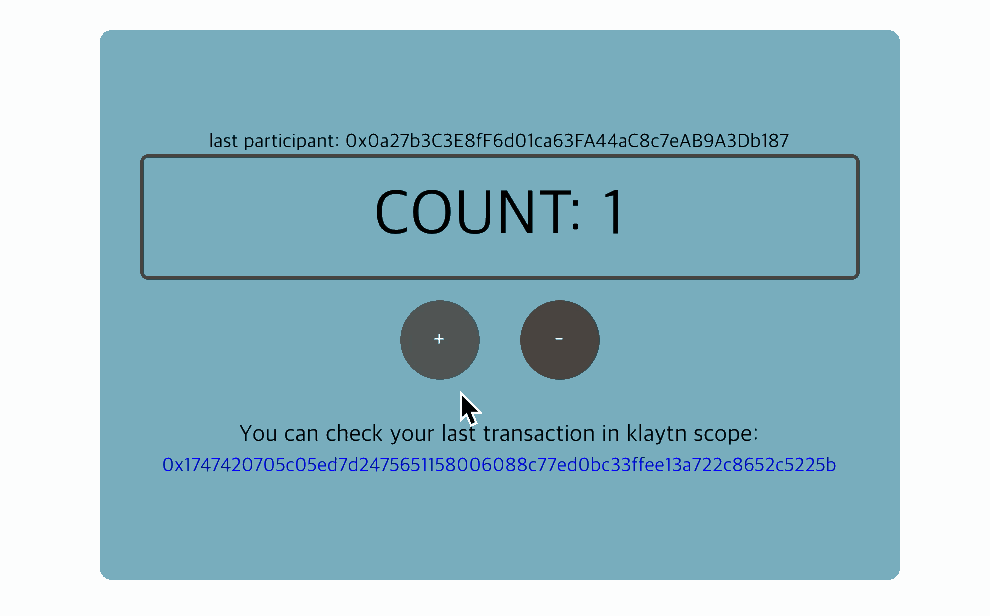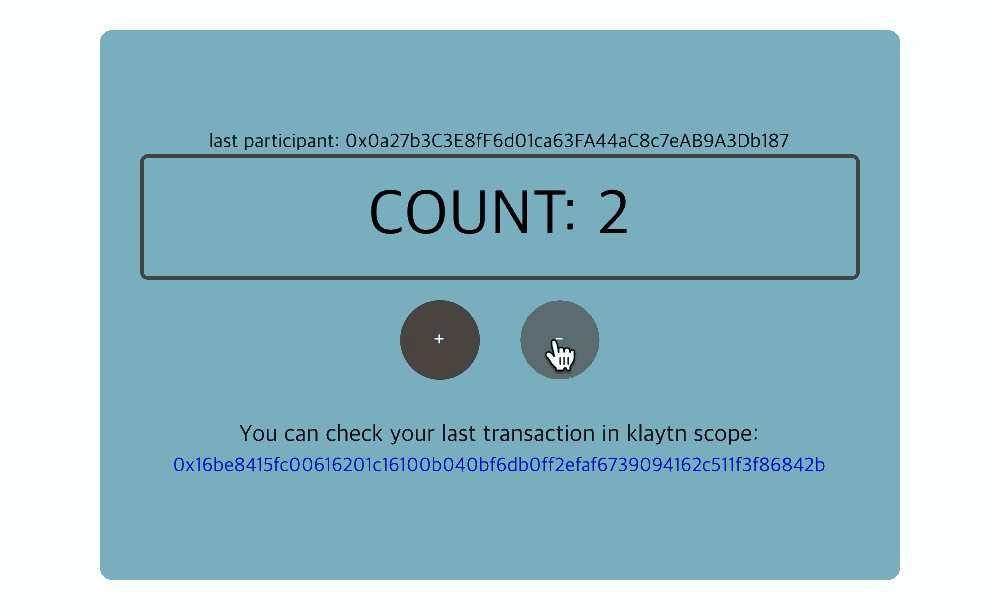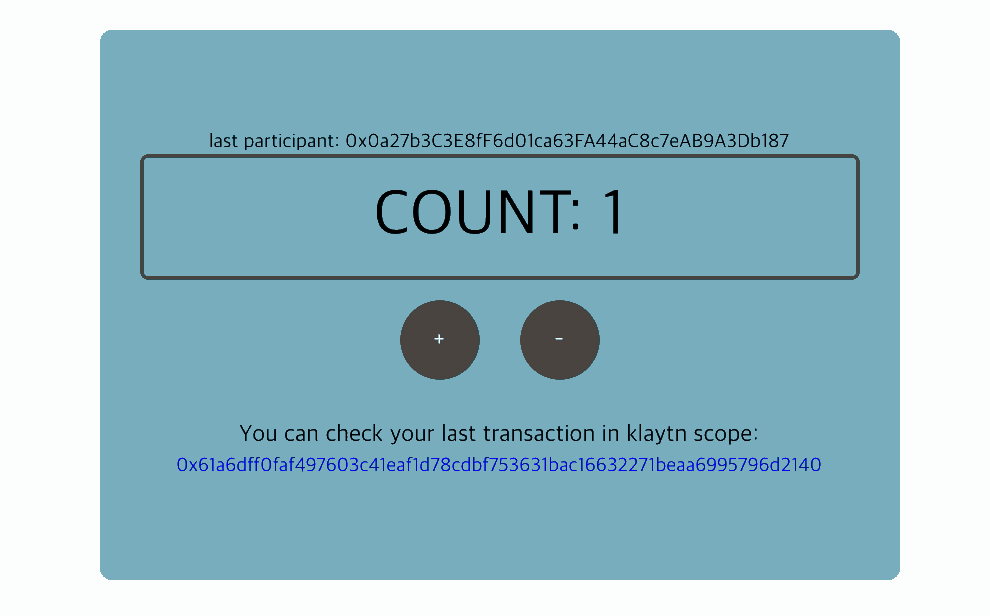
To interact with the contract, we need to create an instance of the deployed contract. With the instance, we can read and write the contract's data.
Let's learn step by step how to migrate CountDApp from Ethereum to Klaytn!
- 5-1. Deploy
Countcontract on Klaytn - 5-2. Create a contract instance
- 5-3. Interact with contract
5-1. Deploy Count contract on Klaytn
The first step is deploying Count contract on Klaytn and get the contract address. Most of the cases, you can use Etherem contracts on Klaytn without modification. See Porting Etherem Contract. In this guide, we will use Truffle to deploy the contract.
- Change network properties in
truffle-config.jsto deploy the contract on Klaytn. - Top up your account using KLAY faucet.
- Type
$ truffle deploy --network baobab --reset Countcontract will be deployed on Baobab testnet, Klaytn.
truffle-config.js
// const HDWalletProvider = require("truffle-hdwallet-provider")const HDWalletProvider = require("truffle-hdwallet-provider-klaytn")// const NETWORK_ID = '3' // Ethereum, Ropsten testnet's network idconst NETWORK_ID = '1001' // Klaytn, Baobab testnet's network id// const RPC_URL = 'https://ropsten.infura.io/'const RPC_URL = 'https://public-en-baobab.klaytn.net'// Change it to your own private key that has enough KLAY to deploy contractconst PRIVATE_KEY = '0x3de0c90ce7e440f19eff6439390c29389f611725422b79c95f9f48c856b58277'module.exports = { networks: { /* ropsten: { provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(PRIVATE_KEY, RPC_URL), network_id: NETWORK_ID, gas: '8500000', gasPrice: null, }, */ baobab: { provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(PRIVATE_KEY, RPC_URL), network_id: NETWORK_ID, gas: '8500000', gasPrice: null, }, }, compilers: { solc: { version: '0.5.6', }, },}
For more details about deploying contracts, See CountDapp tutorial - Deploy Contract.
5-2. Create a contract instance
You can create a contract instance with the caver-js API. The contract instance creates a connection to Count contract. You can invoke contract methods through this instance.
Ethereum :
web3.eth.Contract(ABI, address)
Klaytn :caver.klay.Contract(ABI, address)
src/components/Count.js
// import web3 from 'ethereum/web3'import caver from 'klaytn/caver'class Count extends Component { constructor() { /* const CountContract = DEPLOYED_ABI && DEPLOYED_ADDRESS && new web3.eth.Contract(DEPLOYED_ABI, DEPLOYED_ADDRESS) */ this.countContract = DEPLOYED_ABI && DEPLOYED_ADDRESS && new cav.klay.Contract(DEPLOYED_ABI, DEPLOYED_ADDRESS) } // ...}export default Count
5-3. Interact with contract
The ABI (Application Binary Interface) used to create the Count contract instance allows the caver-js to invoke contract's methods as below. You can interact with Count contract as if it were a JavaScript object.
- Read data (call)
CountContract.methods.count().call() - Write data (send)
CountContract.methods.plus().send({ ... })
CountContract.methods.minus().send({ ... })
Once you created a contract instance as in the previous step, you don't need to modify any code in using the contract methods afterward. dApp migration has been completed!
Full code: Count component
src/components/Count.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'import cx from 'classnames'import caver from 'klaytn/caver'import './Count.scss'class Count extends Component { constructor() { super() // ** 1. Create contract instance ** // ex:) new caver.klay.Contract(DEPLOYED_ABI, DEPLOYED_ADDRESS) // You can call contract method through this instance. // Now you can access the instance by `this.countContract` variable. this.countContract = DEPLOYED_ABI && DEPLOYED_ADDRESS && new caver.klay.Contract(DEPLOYED_ABI, DEPLOYED_ADDRESS) this.state = { count: '', lastParticipant: '', isSetting: false, } } intervalId = null getCount = async () => { // ** 2. Call contract method (CALL) ** // ex:) this.countContract.methods.methodName(arguments).call() // You can call contract method (CALL) like above. // For example, your contract has a method called `count`. // You can call it like below: // ex:) this.countContract.methods.count().call() // It returns promise, so you can access it by .then() or, use async-await. const count = await this.countContract.methods.count().call() const lastParticipant = await this.countContract.methods.lastParticipant().call() this.setState({ count, lastParticipant, }) } setPlus = () => { const walletInstance = caver.klay.accounts.wallet && caver.klay.accounts.wallet[0] // Need to integrate wallet for calling contract method. if (!walletInstance) return this.setState({ settingDirection: 'plus' }) // 3. ** Call contract method (SEND) ** // ex:) this.countContract.methods.methodName(arguments).send(txObject) // You can call contract method (SEND) like above. // For example, your contract has a method called `plus`. // You can call it like below: // ex:) this.countContract.methods.plus().send({ // from: '0x952A8dD075fdc0876d48fC26a389b53331C34585', // PUT YOUR ADDRESS // gas: '200000', // }) this.countContract.methods.plus().send({ from: walletInstance.address, gas: '200000', }) .once('transactionHash', (txHash) => { console.log(` Sending a transaction... (Call contract's function 'plus') txHash: ${txHash} ` ) }) .once('receipt', (receipt) => { console.log(` Received receipt! It means your transaction(calling plus function) is in klaytn block(#${receipt.blockNumber}) `, receipt) this.setState({ settingDirection: null, txHash: receipt.transactionHash, }) }) .once('error', (error) => { alert(error.message) this.setState({ settingDirection: null }) }) } setMinus = () => { const walletInstance = caver.klay.accounts.wallet && caver.klay.accounts.wallet[0] // Need to integrate wallet for calling contract method. if (!walletInstance) return this.setState({ settingDirection: 'minus' }) // 3. ** Call contract method (SEND) ** // ex:) this.countContract.methods.methodName(arguments).send(txObject) // You can call contract method (SEND) like above. // For example, your contract has a method called `minus`. // You can call it like below: // ex:) this.countContract.methods.minus().send({ // from: '0x952A8dD075fdc0876d48fC26a389b53331C34585', // PUT YOUR ADDRESS // gas: '200000', // }) // It returns event emitter, so after sending, you can listen on event. // Use .on('transactionHash') event, // : if you want to handle logic after sending transaction. // Use .once('receipt') event, // : if you want to handle logic after your transaction is put into block. // ex:) .once('receipt', (data) => { // console.log(data) // }) this.countContract.methods.minus().send({ from: walletInstance.address, gas: '200000', }) .once('transactionHash', (txHash) => { console.log(` Sending a transaction... (Call contract's function 'minus') txHash: ${txHash} ` ) }) .once('receipt', (receipt) => { console.log(` Received receipt which means your transaction(calling minus function) is in klaytn block(#${receipt.blockNumber}) `, receipt) this.setState({ settingDirection: null, txHash: receipt.transactionHash, }) }) .once('error', (error) => { alert(error.message) this.setState({ settingDirection: null }) }) } componentDidMount() { this.intervalId = setInterval(this.getCount, 1000) } componentWillUnmount() { clearInterval(this.intervalId) } render() { const { lastParticipant, count, settingDirection, txHash } = this.state return ( <div className="Count"> {Number(lastParticipant) !== 0 && ( <div className="Count__lastParticipant"> last participant: {lastParticipant} </div> )} <div className="Count__count">COUNT: {count}</div> <button onClick={this.setPlus} className={cx('Count__button', { 'Count__button--setting': settingDirection === 'plus', })} > + </button> <button onClick={this.setMinus} className={cx('Count__button', { 'Count__button--setting': settingDirection === 'minus', })} > - </button> {txHash && ( <div className="Count__lastTransaction"> <p className="Count__lastTransactionMessage"> You can check your last transaction in klaytnscope: </p> <a target="_blank" href={`https://klaytnscope.com/tx/${txHash}`} className="Count__lastTransactionLink" > {txHash} </a> </div> )} </div> ) }}export default Count